Flat Foot
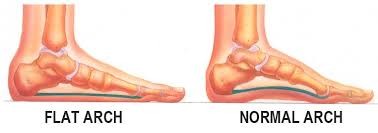
What is flatfoot deformity?
Flat foot deformity in which the longitudinal arch in the foot, which runs along the sole of the foot, has not developed normally and is lowered or flattened out.
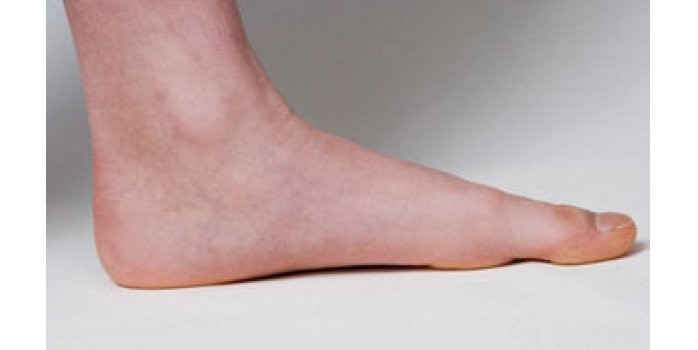
Pes planus may occur in as many as 20% of the adult population. Although, the majority of patients are asymptomatic and require no treatment. Children as well as adults may be flat-footed. Most children are flat-footed until they are between the ages of 3 and 5 when their longitudinal arch develops normally. Boys and overweight children are more subjected to flat feet.
Hyperpronation moves the transmission of force medially as the weight is transferred forwards on to the walking foot. This can stretch the soft tissues behind the medial malleolus.
What are causes of flatfoot?
A person may be born with a flatfoot or develop it as an adult. Causes of flatfoot include the following:
- Trauma
- Obesity (Obesity in children is significantly correlated with flat feet in early childhood)
- Diabetes
- pregnancy, due to hormonal changes such as increases in Elastin
- Age
- Arthritis (Inflammatory arthritis, such as rheumatoid arthritis, can cause a painful flatfoot)
- Tarsal bone coalitions: this condition is less common cause of flat feet, that foot joints grow together restricting movement of that joint.
- Posterior tibia tendon dysfunction
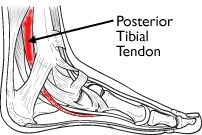
- Ligament laxity in diseases
What are flatfoot symptoms and signs?
Depending on the cause of the flatfoot, a patient may experience different symptoms below:
- pain that may be in the inside arch, heel, or ankle
- Rolling in of the foot and ankle and tilting outward of the heel.
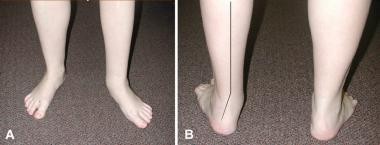
- shin pain
- Aching of the knee, hip, and/or lower back.
- Earlier fatigue during walking
- Pain that is worse with activity.
- Pain during standing for long periods of time.
What is the treatment for flatfoot?
Treatment depends on the type of flatfoot, its stage of progression, and the symptoms including:
- Proper shoe with proper arch support
- Medical insole
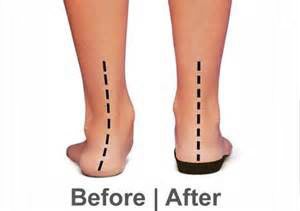
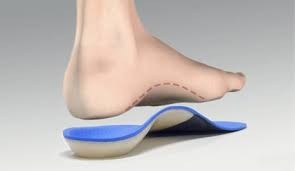
- Custom functional orthotics
- Non-steroid drugs
- Weight loss in patients with obesity
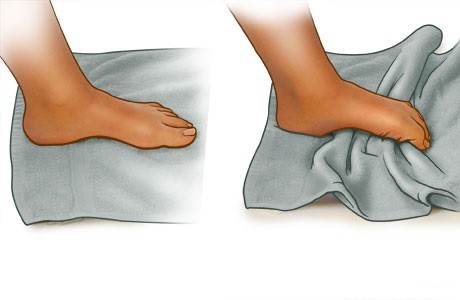
- Exercises to strengthen foot muscles
- Toes curl exercise: While sitting, place your foot on a towel on the floor and scrunch the towel toward you with your toes
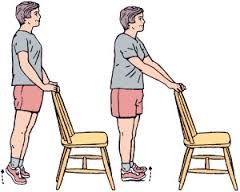
- Heel raises (standing on tiptoe).
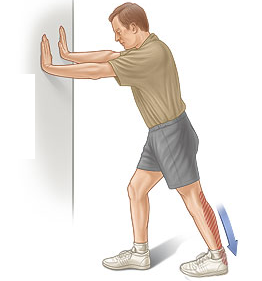
- Stand facing a wall with your hands on the wall at about eye level. Put the leg you want to stretch about a step behind your other leg. Bend your front knee until you feel a stretch in the back leg. Hold the stretch for 15 to 30 seconds. Repeat 2 to 4 times.
Your comment successfully stored, thanks. Unfortunately comment storage process failed.